Key takeaways
Knowing the most important lessons from reverse logistics is essential for supply chain management. Managing the movement of goods from the point of consumption back to the place of origin while paying attention to returns, repairs, recycling, and other issues is the main goal of reverse logistics. Businesses may limit environmental impact, cut expenses, and recover value from returned items by utilizing reverse logistics tactics successfully. Reverse logistics’ seven Rs—returns, refurbishing, redistribution, recycling, repair, remarketing, and replenishment—offer a thorough structure for handling the reverse flow. By putting these concepts into practice, one may gain a competitive edge as well as increased customer happiness, cost savings, environmental sustainability, and supply chain efficiency. Although there are obstacles to overcome, such as poor visibility, quality control, data management, and transportation, there are also tools at our disposal to assist us do so, including technology, collaboration, quality control procedures, and data analytics. Future developments in reverse logistics indicate a greater emphasis on sustainability and technology breakthroughs, which will influence the direction of the sector going forward.
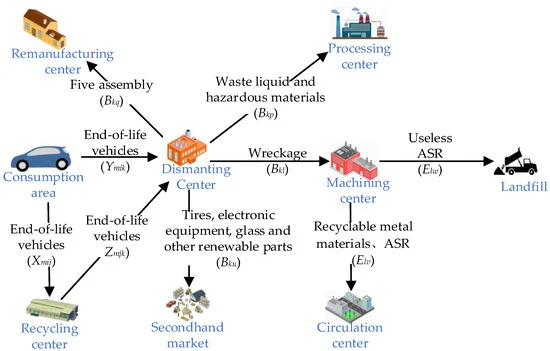
Reverse logistics is a vital idea in today’s fast-paced business environment, as it helps maximize the value of items that have reached the end of their lifetime. Businesses may recover value from returned items, cut expenses, and lessen their environmental effect by managing the reverse flow of goods efficiently. Companies may ensure that they manage product returns, refurbishing, redistribution, recycling, repair, remarketing, and restocking effectively by adhering to the complete structure provided by the 7 R’s of reverse logistics. Businesses may get a competitive edge by putting these methods into practice and improving customer happiness, cost reduction, sustainability, and inventory management. While obstacles like poor visibility and problems with quality control may occur during the reverse logistics process, businesses can get past these problems by utilizing technology, putting strong quality control procedures in place, working with partners, and using data analytics to make well-informed decisions. Trends indicate that reverse logistics will continue to be shaped by technology improvements and a greater emphasis on sustainability as the sector develops.
The Essence of Reverse Logistics
The process of controlling the movement of goods from the point of consumption back to the point of origin is known as reverse logistics. In contrast to traditional logistics, which concentrates on the forward movement of commodities, reverse logistics handles product returns, repairs, recycling, and other related tasks.
Reverse logistics’ capacity to optimize the value of returned or end-of-life goods is what makes it fundamental. Businesses may limit environmental impact, cut expenses, and recover value from returned items by managing the reverse flow properly.
Reverse logistics includes a range of tasks, such as product disposal, recycling, refurbishing, and returns. Coordinating with suppliers, clients, and other relevant parties is necessary to guarantee effective and long-lasting handling of returned goods.
Supply chain management now requires reverse logistics as a crucial component in the cutthroat economic environment of today. Reverse logistics techniques give businesses a competitive edge by cutting expenses, raising customer happiness, and strengthening sustainability.
Reverse logistics is fundamentally about optimizing the whole lifespan of a product and generating value from the movement of things in the opposite direction.
The 7 R’s Unveiled
A thorough structure known as the “7 R’s of reverse logistics” offers direction for handling the product flow in reverse. Each R stands for an important component that businesses using reverse logistics solutions have to take into account. Let’s examine each R in more depth:
1. Returns: The management of product returns is the main topic of this R. It entails defining precise return guidelines, offering consumers easy return procedures, and putting in place effective mechanisms for managing returned goods.
2. Refurbishment: Refurbishment is the process of fixing and reconditioning returned goods to make them suitable for sale. This R highlights how crucial it is to put in place effective refurbishing procedures in order to maximize the value of returned goods.
3. Redistribution: The practice of reassigning returned goods to the proper places throughout the supply chain is known as redistribution. This R emphasizes how important it is to maximize the reverse flow in order to save transportation expenses and guarantee timely redistribution.
4. Recycling: Recycling is the process of disposing of end-of-life goods in an ecologically friendly manner. This R highlights how crucial it is to put into practice sustainable recycling techniques in order to cut down on trash and lessen the effect on the environment.
5. Repair: To prolong the life of a product, repair entails correcting flaws or damage. This R emphasizes how crucial it is to put in place effective repair procedures in order to save expenses and optimize the value of returned goods.
6. Remarketing: This is the process of reselling returned goods that are still in marketable shape. This R highlights how crucial it is to put into practice efficient remarketing techniques in order to maximize the value of returned goods and reduce monetary losses.
7. Replenishment: Resupply is the process of restocking inventories using the knowledge gathered from reverse logistics operations. This R emphasizes how crucial it is to use information from returns and other reverse flow operations to improve inventory control.
Companies may optimize their supply chain management and develop a complete strategy for controlling the reverse flow of products by comprehending and putting into practice the seven Rs of reverse logistics.
Benefits of Implementing the 7 R’s
Companies can gain greatly from the use of the seven rules of reverse logistics. Among the main advantages are:
– Enhanced customer satisfaction: Businesses may boost customer satisfaction and loyalty by offering easy return procedures and effective management of returned goods.
– Cost reduction: Lowering the price of returns, repairs, and disposal is possible with efficient reverse logistics management. It enables businesses to reduce losses and recoup value from returned goods.
– Environmental sustainability: To limit waste and lessen environmental effect, the 7 R’s framework highlights the significance of implementing sustainable practices, such as recycling and refurbishing.
– Increased supply chain efficiency: The supply chain’s overall efficiency may be raised by optimizing the products’ reverse flow through the seven R’s. It helps businesses to streamline procedures, lower transportation costs, and improve inventory management.
– Competitive advantage: Businesses may obtain a competitive edge by putting the 7 R’s of reverse logistics into practice. By providing better customer service, cutting expenses, and showcasing their dedication to sustainability, they may set themselves apart.
All things considered, putting the 7 R’s of reverse logistics into practice may result in increased customer happiness, lower costs, and better operational efficiency—all of which can ultimately propel corporate success.
Challenges and Solutions in Reverse Logistics
Reverse logistics has many advantages, but it also has a unique set of difficulties. Typical difficulties in reverse logistics include the following:
– Lack of sight: Controlling the flow of items backwards can be difficult, particularly if there is little visibility throughout the whole supply chain. Return processing delays and inefficiencies may arise from this.
– Quality control: It might be difficult to guarantee the caliber and state of returned goods. To find and fix any problems, thorough inspection and testing procedures must be put in place.
– Logistics and transportation: Compared to conventional forward logistics, the reverse flow of items frequently necessitates distinct logistics and transportation arrangements. In order to keep expenses down and guarantee timely redistribution, effective logistics and transportation management is essential.
– Data management: A lot of data is produced by reverse logistics, including details on client preferences, repairs, and returns. It can be difficult to manage and analyze this data without the appropriate tools and methods.
Businesses can use a range of strategies to address these issues, such as:
– Better visibility through technological means: Making use of cutting-edge technologies, such data analytics and real-time tracking systems, may facilitate more effective management and offer better visibility into the product’s reverse flow.
– Sturdy quality control procedures: Enforcing strict testing and inspection procedures may assist guarantee the caliber and state of returned goods. This enables businesses to recognize any problems and take the necessary action.
– Cooperation with partners: Reverse logistics may be streamlined by forming solid alliances with suppliers, logistics companies, and other stakeholders. Better coordination and quicker problem solving are made possible through collaboration.
– Data analytics for decision-making: Businesses may learn from reverse logistics data by utilizing data analytics tools and methodologies. This makes it possible to optimize operations and make decisions based on data.
Through the identification and implementation of appropriate solutions, organizations may surmount the intricacies of reverse logistics and optimize its advantages.
Future Trends in Reverse Logistics
Future developments in reverse logistics are anticipated to follow a number of patterns as the business environment keeps changing. Among the prominent trends are:
– A greater emphasis on sustainability: As environmental concerns develop, businesses are probably going to give sustainable reverse logistics methods more of a priority. This include encouraging recycling, renovation, and environmentally responsible disposal techniques.
– Technological developments: It is anticipated that reverse logistics will undergo a radical transformation thanks to developments in artificial intelligence (AI), blockchain, and the Internet of Things (IoT). These technologies can improve visibility, automate procedures, and allow for more effective product flow management in reverse.
– Growing importance of circular economy: The concept of a circular economy, which aims to minimize waste and maximize resource efficiency, is gaining traction in reverse logistics. Companies are increasingly adopting circular economy principles to optimize the recovery of value from returned products.
– Reverse logistics as a source of competitive advantage: As companies realize the potential of reverse logistics to drive customer satisfaction, cost reduction, and sustainability, it is likely to become a source of competitive advantage. Those who effectively manage the reverse flow of products can differentiate themselves in the market.
– Integration of reverse logistics with forward logistics: The integration of reverse logistics with forward logistics is expected to become more seamless in the future. Better coordination, more visibility, and greater supply chain performance are all possible outcomes of this connection.
Businesses should proactively adjust their reverse logistics strategy and maintain an advantage over rivals by keeping up with these emerging trends.
To sum up, supply chain management’s reverse logistics component is essential as it addresses the movement of goods in the other direction. Through comprehension of the fundamentals of reverse logistics and use of the 7 R’s framework, businesses may optimize their supply chain, save expenses, raise customer contentment, and increase sustainability. Reverse logistics has several advantages despite its difficulties, and the sector is expected to grow in an interesting way. Businesses may fully realize the benefits of reverse logistics and obtain a competitive advantage by adopting these trends and putting appropriate solutions into place. in the market.
In summary, the 7 R’s of reverse logistics provide businesses with a thorough framework to efficiently manage product movement in reverse and enhance supply chain efficiency. Businesses may increase customer happiness, save costs, promote sustainability, and gain a competitive edge by giving refurbishing, redistribution, recycling, repair, remarketing, and restocking top priority. While problems with data management, transportation logistics, quality control, and lack of visibility may occur, they may also be solved with the aid of technological integration, strong quality control procedures, partner cooperation, and data analytics. Future developments in reverse logistics suggest that sustainability, technology breakthroughs, circular economy ideas, and the merging of reverse and forward logistics will receive more attention. Businesses may proactively shape these trends by being informed and making adjustments as needed. their reverse logistics strategies and stay ahead of the competition in the evolving business landscape.

FAQ
What are the 7 R’s of reverse logistics?
A key framework for businesses to manage the reverse flow of products in their supply chain activities is the 7 R’s of reverse logistics. Refurbishment, redistribution, recycling, repair, remarketing, and replenishment are some of these “R’s.” In order to handle returned goods as efficiently as possible, increase customer happiness, cut expenses, improve sustainability, and obtain a competitive edge, each R is crucial. Businesses may develop a thorough strategy for reverse logistics that promotes operational effectiveness and company success by giving these R’s top priority.
What are the 7 R’s of logistics management?
A vital framework that includes the fundamental ideas for efficiently controlling the flow of goods in the supply chain is the “7 R’s of logistics management.” These R’s encompass not just the forward logistics concepts of resourcefulness, responsiveness, and resilience, but also the reverse logistics principles of replenishment, redistribution, recycling, repair, and remarketing. Businesses may increase customer happiness, cut expenses, boost sustainability, streamline their supply chains, and gain a competitive edge by incorporating these ideas into their daily operations. Throughout the whole logistics process, each R is essential to ensuring that items are handled well, waste is reduced, and value is maximized. By adopting the seven pillars of logistics management, companies may develop a thorough and well-thought-out strategy for both forward and reverse logistics, ultimately driving operational efficiency and business success.
What are the 7 C’s of logistics?
Businesses may enhance their supply chain operations by adhering to the 7 C’s of logistics. Coordination, communication, consistency, teamwork, customisation, cost-effectiveness, and customer satisfaction are some of these Cs. Companies can make sure that their logistics processes are well-coordinated, that communication is clear and effective, that operations are consistent and dependable, that partner collaboration is seamless, that solutions are tailored to meet specific needs, that costs are effectively managed, and that customer satisfaction is given priority by concentrating on these principles. Businesses may develop a strong and strategic approach to supply chain management by embracing the seven C’s of logistics, which will increase operational effectiveness and overall market performance.
What are the reverse logistics RS?
The term “reverse logistics” (RS) describes the essential tactics and procedures used in the supply chain to control the movement of goods in reverse. These RS techniques are essential for streamlining the processing of returned goods, cutting expenses, raising customer happiness, and strengthening sustainability. Businesses may efficiently manage the reverse logistics (RS) framework to increase operational efficiency and obtain a competitive advantage in the market by concentrating on refurbishing, redistribution, recycling, repair, remarketing, and restocking. Businesses may develop a thorough and systematic approach to reverse logistics by adopting these RS concepts, which will eventually result in corporate success and development.
Hope this article was helpful for more checkout our previous blog post by clicking here.

