Shipping containers have revolutionized the transportation industry, providing a standardized and efficient method for moving goods across different modes of transportation. These large, rectangular steel boxes have transformed multi-modal transportation, enabling faster, more reliable, and cost-effective delivery of goods.

Source: Alliance Logistics
In this article, we will delve into the history and impact of shipping containers on the transportation industry, exploring their benefits, different types, and the promising future they hold.
The Evolution of Shipping Containers
Before the advent of shipping containers, cargo transportation was a time-consuming and labor-intensive process. Goods were individually loaded and unloaded from ships, trains, and trucks, often resulting in delays, damage, and high costs. The introduction of shipping containers in the 1950s changed this landscape dramatically.

Malcom McLean, an American entrepreneur, is credited with pioneering the use of standardized shipping containers. In 1956, McLean’s company, Sea-Land Service, loaded 58 aluminum shipping containers onto a converted oil tanker, the Ideal X, for a voyage from Newark to Houston. This marked the birth of modern container shipping. Recognizing the potential of this innovation, the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) later established standard sizes for shipping containers, primarily 20 and 40 feet in length, ensuring compatibility across different modes of transportation.
Key Statistics:
- In 2021, the global container shipping market was valued at approximately $11.31 billion, and it is projected to reach $14.93 billion by 2026, growing at a CAGR of 5.7% from 2021 to 2026 (source: MarketsandMarkets).
- As of 2021, China was the largest container shipping market, accounting for around 30% of the global container throughput (source: UNCTAD).
- According to the World Shipping Council, approximately 226 million TEUs (twenty-foot equivalent units) were moved by container shipping in 2021.
Efficiency and Cost-Effectiveness of Multi-Modal Transportation
The standardization of shipping containers has played a pivotal role in making multi-modal transportation more efficient and cost-effective. By providing a uniform size and shape for cargo, containers simplify the loading and unloading process across various transportation modes. This reduces handling time and costs while minimizing the risk of damage during transfers.
Moreover, shipping containers enable efficient use of space on ships, trains, and trucks. Their stackability allows for maximizing capacity, optimizing logistical operations, and reducing the need for multiple trips. This streamlined approach not only saves time but also lowers fuel consumption, making container shipping more environmentally friendly.
Key Statistics: According to a study by the United Nations Conference on Trade and Development (UNCTAD), the average port stay time for container ships decreased from around 3.7 days in 2005 to 1.5 days in 2021, largely due to the efficiencies brought about by containerization.
Benefits of Using Shipping Containers in Transportation
The use of shipping containers in transportation offers numerous benefits for various stakeholders in the global supply chain.
Source: BrightPearl
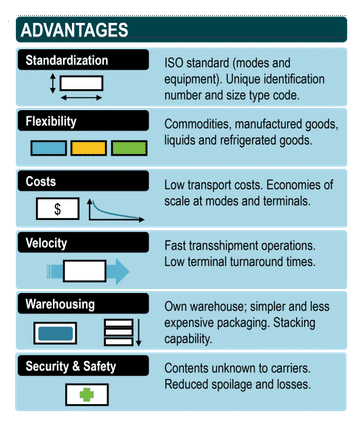
- Standardization: The uniformity in container sizes enables efficient handling across different modes of transportation, ensuring seamless transfer and reducing delays.
- Security: Shipping containers can be easily sealed and secured, protecting goods from theft and damage while in transit.
- Flexibility: Containers can be loaded with diverse types of cargo, ranging from electronics to perishable goods, offering versatility in transportation.
- Intermodal Compatibility: Containers can seamlessly transition between ships, trains, and trucks, facilitating intermodal transportation and enabling door-to-door delivery.
- Reduced Costs: The efficiency and economies of scale achieved through containerization have resulted in significant cost reductions in transportation, benefiting both producers and consumers.
- Environmental Impact: Container shipping, by consolidating goods and optimizing logistical operations, reduces the overall carbon footprint of transportation, contributing to sustainability goals.
Key Statistic: According to a report by the World Shipping Council, the average carbon dioxide emissions per TEU-kilometer for container ships decreased by 46% between 2008 and 2018.
Types of Shipping Containers

A variety of container types cater to the specific needs of different types of cargo and transportation requirements:
- Standard Dry Containers: These are the most commonly used containers for general cargo such as electronics, clothing, and furniture. They are weatherproof and protect goods from external elements.
- Refrigerated Containers: Also known as “reefers,” these containers are equipped with temperature control systems, enabling the transport of perishable goods like fruits, vegetables, and pharmaceuticals.
- Open-Top Containers: Designed for oversized cargo that cannot fit through standard container doors, these containers have removable tops, making it easier to load and unload bulky items.
- Flat Rack Containers: Used for heavy machinery, vehicles, and other large equipment, flat rack containers have collapsible sides, facilitating loading from the sides or top.
- Specialized Containers: Hazardous materials, livestock, and other specialized cargo require containers designed specifically for their unique requirements. These containers adhere to strict safety regulations and ensure the well-being of both cargo and transportation personnel.
The Future of Shipping Containers in Transportation
The future of shipping containers in transportation appears promising as they continue to evolve and adapt to the changing needs of global trade.
- Technological Advancements: With the integration of sensors, tracking systems, and Internet of Things (IoT) technologies, shipping containers are becoming more secure, trackable, and interconnected. Real-time monitoring systems enable improved inventory management and more efficient logistics planning.
- Durability and Sustainability: Ongoing research and development focus on creating containers that are lighter, more durable, and environmentally friendly. Innovations in materials, such as composite alloys and advanced coatings, enhance container longevity and reduce maintenance requirements.
- Automation and Robotics: Automated container handling systems and robotic technologies are being implemented in ports and terminals, further streamlining operations and reducing human error. This automation enhances the speed and efficiency of container transfers.
- Smart Containers: Emerging technologies, such as smart containers equipped with IoT sensors, offer real-time monitoring of temperature, humidity, and location. This enhances cargo safety, reduces spoilage, and improves supply chain visibility.
- Intermodal Connectivity: The integration of different modes of transportation, including rail, road, and inland waterways, is expected to enhance intermodal connectivity, reducing transit times and costs.
Shipping containers have revolutionized the transportation industry, providing standardized, efficient, and cost-effective multi-modal transportation solutions. Through their role in streamlining cargo handling, optimizing space utilization, and reducing environmental impact, shipping containers have become an integral part of global trade. As technology continues to advance and sustainable practices gain prominence, shipping containers will remain a vital component of the evolving transportation landscape, enabling seamless movement of goods across the world.
Key Takeaways:
1. Shipping containers have transformed multi-modal transportation by providing a standardized and efficient method for moving goods across different modes of transportation.
2. The introduction of shipping containers in the 1950s revolutionized cargo transportation, simplifying the loading and unloading process and reducing delays, damages, and costs.
3. Standardization of container sizes has made multi-modal transportation more efficient and cost-effective by simplifying handling and reducing the risk of damage during transfers.
4. Shipping containers enable efficient use of space on ships, trains, and trucks, maximizing capacity, optimizing logistical operations, and reducing the need for multiple trips.
5. The use of shipping containers offers benefits such as standardization, security, flexibility, intermodal compatibility, reduced costs, and environmental impact reduction.
6. Various types of shipping containers cater to different cargo and transportation requirements, including standard dry containers, refrigerated containers, open-top containers, flat rack containers, and specialized containers.
7. The future of shipping containers in transportation looks promising with technological advancements, increased durability and sustainability, automation and robotics, smart container technology, and enhanced intermodal connectivity.
8. Shipping containers will remain a vital component of the evolving transportation landscape, enabling seamless movement of goods across the world as technology continues to advance and sustainable practices gain prominence.
Visit our Blog for more logistics insights, tips and news

